Why Are My Gums White?
Key Facts
- Healthy gums are light pink, firm, and don’t bleed during brushing.
- White gums, white spots on gums, or white line on gums may signal irritation or infection.
- Gingivitis white gums are caused by plaque buildup and can be reversed with proper oral care.
- Oral thrush leads to white patches on gums that can be wiped off.
- Leukoplakia causes thick, white patches that may signal white gums cancer risk.
- Anemia and vitamin deficiencies can result in pale gums or gums turning white.
- Harsh products or aggressive brushing may cause white gums after brushing.
- Autoimmune disorders like lichen planus may lead to receding white gums and mouth sores.
Have you ever looked in the mirror and wondered, “Why are my gums white?” Healthy gums are usually light pink, so noticing white gums or white spots on gums can be alarming. While it may be harmless in some cases, it could also be a sign of an underlying condition that needs attention.
In this blog, we will clearly explain what causes white gums, what they might mean for your health, how to treat them naturally or medically, and when to seek professional help. We’ll also include helpful statistics, pictures, FAQs, and natural prevention tips to guide you.
Table of Contents
Healthy Gums vs Unhealthy Gums
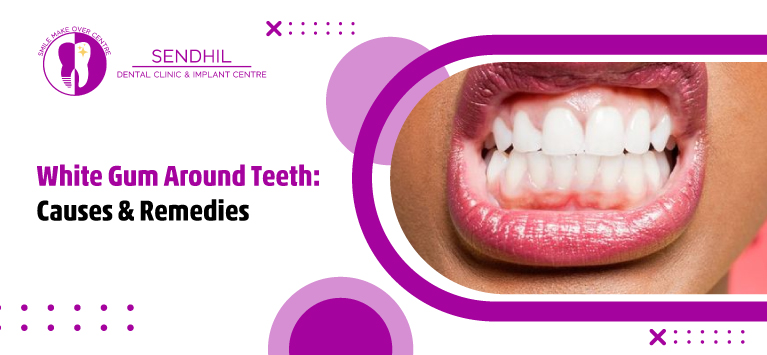
Healthy gums are firm, pale pink, and do not bleed when brushing. They fit snugly around your teeth. In contrast, unhealthy gums may appear red, swollen, receding, or discolored. When you notice white gums, white gums around teeth, or even a white line on gums below teeth, it usually indicates irritation, infection, or a deeper health issue.
Unhealthy gums can progress to gum disease or even tooth loss if not treated early. Comparing normal pictures of healthy gums with pictures of white gums in adults can help you recognize abnormalities early.
Common Causes of White Gums
1. Gingivitis and White Gums
Gingivitis white gums happen when plaque buildup irritates the gum tissue. It may cause pale gums, swelling, bleeding, and white on gums near the teeth. This early stage of gum disease is reversible with proper care.
2. Oral Thrush (Fungal Infection)
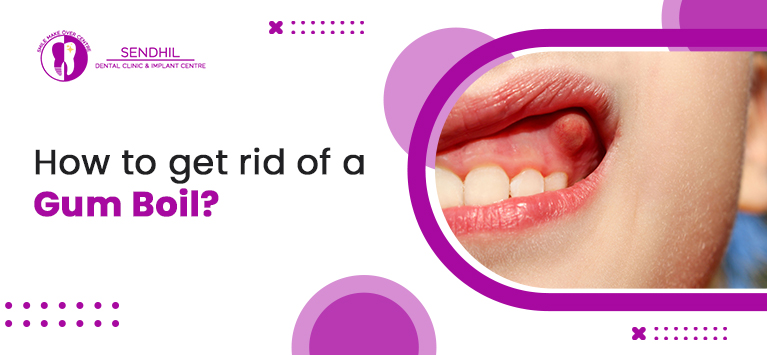
Oral thrush is caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungus, leading to white bump on gums or white spots on gums that can be wiped off. It often affects those with weakened immunity or who use antibiotics frequently.
3. Leukoplakia and Oral Cancer
White gums cancer or leukoplakia causes thick, white patches that don’t rub off. These patches can sometimes become cancerous. This condition needs medical evaluation, especially if you also notice early gum cancer pictures showing persistent, irregular patches.
4. Anemia and Nutrient Deficiencies
Low levels of iron, folate, or vitamin B12 may result in pale gums or gums turning white. Anemia can also cause fatigue, dizziness, and skin paleness. A blood test is required to confirm and correct these deficiencies.
5. Whitening Products and Irritants
Overuse of whitening strips or harsh toothpaste can cause irritation and create a white line on gums below teeth. If you’re wondering why are my gums white after brushing, the reason may be brushing too hard or using abrasive products.
6. Autoimmune Conditions
Diseases like lichen planus or lupus may cause gums to turn white due to inflammation. In these cases, gums turning white and receding may occur along with sores or discomfort.
- In India, around 50-85% of adults suffer from gum issues.
- 45% of adults aged 30+ show signs of periodontal disease.
- Nearly 70% of adults over 65 have gum disease.
Pictures of White Gums vs Normal Gums
Visuals help spot the difference between healthy and problematic gums. Normal pictures of healthy gums look uniformly pink, smooth, and tight around the teeth. Pictures of white gums may show signs like:
- Flat or raised white patches
- Pale, receding gums
- White ulcers or bumps
- White gums around teeth


Symptoms That May Accompany White Gums
- Swelling or tenderness
- Bad breath
- Bleeding when brushing
- Receding gum line
- Fatigue (if related to anemia)
- Sores or blisters
- Persistent white spots on gums
How to Get Rid of White Gums Naturally and Medically
Home Remedies:
- Salt water rinse: Reduces bacteria and soothes irritation.
- Coconut oil pulling: Natural antimicrobial.
- Eat iron and B12-rich foods: Spinach, fish, eggs.
- Stay hydrated: Keeps the mouth clean.
- Switch to soft toothbrush and gentle toothpaste: Avoid harsh brushing.
Medical Treatments:
- Antifungal medication: For oral thrush.
- Mouthwash or antibiotics: For bacterial gum disease.
- Biopsy or removal: For leukoplakia or suspicious patches.
- Dental cleaning: To remove tartar and treat gingivitis.
Knowing how to get rid of white gums starts with identifying the cause. If symptoms last more than 2 weeks, visit your dentist.
Prevention Tips
- Brush twice a day and floss once daily.
- Avoid smoking and tobacco use.
- Limit alcohol and sugar intake.
- Use fluoride toothpaste and antibacterial mouthwash.
- Visit your dentist every 6 months.
Over 3.9 billion people worldwide are affected by oral diseases.
Conclusion
To summarize, if you’ve been asking “Why are my gums white?”, the answer could range from minor irritation to serious health conditions like gingivitis white gums, white gums cancer, or anemia. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding what white gums meaning is key to maintaining good oral health. Whether it’s white bump on gums, white spots on gums, or white gums around teeth, it’s important not to ignore them. Always compare your symptoms with normal pictures of healthy gums and consult a professional if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
It’s often caused by plaque buildup, irritation from brushing, or early gum disease.
Localized irritation, a trapped food particle, or early infection may cause this.
Use salt water rinses, coconut oil pulling, and brush gently with a soft brush.
Yes, overuse or improper application can irritate and whiten your gum tissue.
Possible reasons include infection, irritation, anemia, or gum disease.
Gum whiteness may come from thrush, leukoplakia, brushing too hard, or nutritional issues.
Likely due to harsh brushing or reaction to abrasive toothpaste or whitening agents.